





tags to create section headings and tags where needed.
Include a link to your ‘Prebuilt Courses’ section on your site where people can order a course to be customized based on over 20 topics. You build custom solutions and offer these courses as a way to quickly fill a client’s portfolio of online courses for employees or solopreneur content creators. People can get a prebuilt course in only a few days using your white glove service. Here is a link to the cataloghttps://an802adam.biz/all-courses.
Make sure to end the blog article with a link to the source content originally titled: The Role of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) in eLearning
For example: If you would like to read more about this topic, check out the source here: [original title]
The source URL to link to is: https://elearning.adobe.com/2025/03/the-role-of-virtual-reality-vr-and-augmented-reality-ar-in-elearning/
Here is the content to rewrite: Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of education, technology has consistently played a transformative role. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) have emerged as game-changers, redefining how learners engage with content. By creating immersive, interactive, and experiential learning environments, VR and AR are bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. Here’s a closer look at how these technologies are shaping the eLearning landscape.
What Are VR and AR?
- Virtual Reality (VR) creates fully immersive experiences by simulating environments where learners can interact with digital objects and scenarios using devices like headsets and controllers. It is particularly useful in creating realistic simulations, allowing learners to explore scenarios that would otherwise be difficult or unsafe to replicate in real life.
- Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital elements like images, sounds, or texts onto the real world using devices such as smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses. Unlike VR, AR enhances the physical environment, blending real and virtual elements.
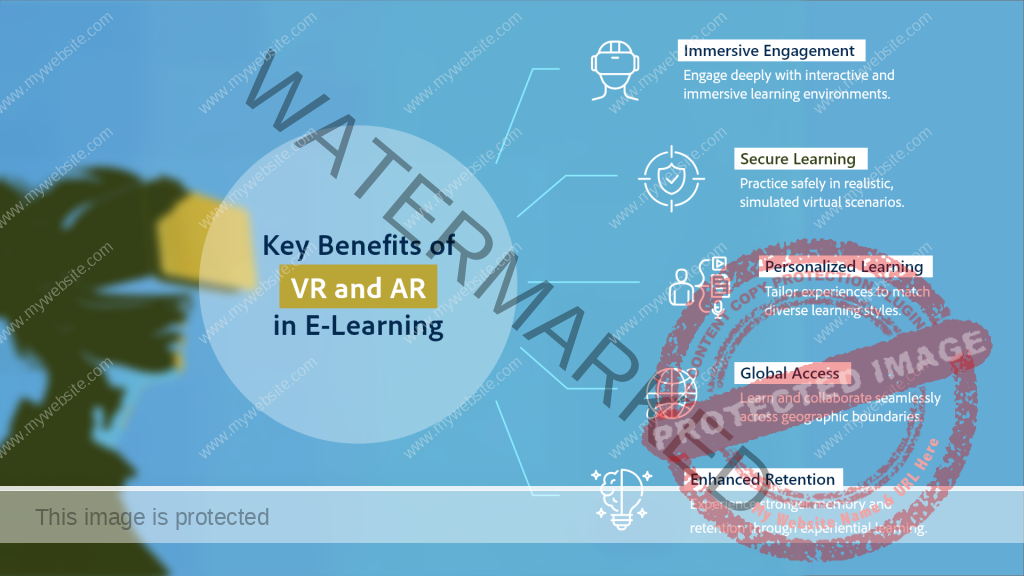
Key Benefits of VR and AR in eLearning
- Immersive Engagement
Traditional eLearning platforms rely heavily on text, images, and videos. While effective, these formats often lack the interactivity necessary to sustain learner interest. VR and AR introduce immersive environments where learners are not just passive recipients but active participants.
For instance, a medical student can practice surgical procedures in a VR simulation, or a history student can explore an ancient civilization through AR-enhanced environments. Such experiences make learning more engaging and memorable.
- Safe Learning Environments
VR provides a risk-free platform for practicing high-stakes skills. Industries such as aviation, healthcare, and construction leverage VR for simulation-based training, where learners can make mistakes without real-world consequences. AR, on the other hand, provides real-time guidance and feedback in actual environments, enhancing on-the-job training.
- Personalized Learning
VR and AR cater to diverse learning styles. Kinesthetic learners, for example, thrive in environments where they can manipulate and interact with objects, a feature central to both VR and AR. Furthermore, these technologies allow instructors to tailor content based on learner performance, offering adaptive and personalized experiences.
- Global Access
Geographical boundaries no longer restrict learners. With VR and AR, students from around the globe can explore museums, attend virtual conferences, or collaborate in virtual classrooms. This democratization of education ensures equitable access to high-quality resources.
- Enhanced Retention Rates
Experiential learning improves retention. VR and AR create scenarios where learners can apply theoretical knowledge in practical settings, reinforcing learning outcomes. For example, AR applications in anatomy allow students to visualize and interact with 3D models of human organs, which is far more effective than studying 2D diagrams.
Applications of VR and AR in eLearning
- Corporate Training
Companies use VR to simulate challenging workplace scenarios, such as customer interactions or emergency drills. AR is utilized for just-in-time learning, where workers receive step-by-step guidance through AR-enabled devices.
- STEM Education
In science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, VR enables students to conduct experiments in virtual labs, while AR provides real-time visualizations of complex equations and models.
- Language Learning
VR immerses learners in virtual environments where they can practice conversational skills with AI-driven avatars. AR apps overlay translations or contextual information onto real-world objects, enhancing vocabulary acquisition.
- Cultural Exploration
Through VR, learners can virtually visit historic sites, experiencing cultures firsthand. AR enriches these experiences by overlaying historical information, animations, or audio guides onto the real world.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their advantages, VR and AR face certain challenges:
- Cost: High-quality VR headsets and AR devices can be expensive, making them inaccessible for some institutions.
- Technical Expertise: Developing VR and AR content requires specialized skills, which can be a barrier for smaller organizations.
- User Comfort: Extended use of VR headsets can lead to discomfort or motion sickness, which may hinder learning.
- Device Compatibility: AR applications often require modern smartphones or tablets, limiting access for users with older devices.
Future Trends in VR and AR eLearning
- AI Integration: Combining AI with VR and AR will allow for more intelligent and adaptive learning systems, tailoring content to individual needs and preferences.
- Haptic Feedback: The inclusion of haptic devices will enable learners to feel textures and movements in VR, enhancing the realism of simulations.
- 5G Connectivity: The widespread adoption of 5G will reduce latency, enabling smoother and more responsive VR and AR experiences.
- Collaborative VR/AR: Virtual classrooms and AR-enhanced group projects will foster collaboration among learners from diverse locations.
Conclusion
VR and AR are revolutionizing eLearning by making it more interactive, engaging, and effective. While challenges remain, the potential benefits far outweigh the limitations. As technology becomes more accessible and affordable, VR and AR are poised to become integral components of mainstream education, transforming how knowledge is delivered and absorbed. For learners and educators alike, the future of learning is not just digital—it’s immersive.
Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of education, technology has consistently played a transformative role. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) have emerged as game-changers, redefining how learners engage with content. By creating immersive, interactive, and experiential learning environments, VR and AR are bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. Here’s a closer look at how these technologies are shaping the eLearning landscape.
What Are VR and AR?
- Virtual Reality (VR) creates fully immersive experiences by simulating environments where learners can interact with digital objects and scenarios using devices like headsets and controllers. It is particularly useful in creating realistic simulations, allowing learners to explore scenarios that would otherwise be difficult or unsafe to replicate in real life.
- Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital elements like images, sounds, or texts onto the real world using devices such as smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses. Unlike VR, AR enhances the physical environment, blending real and virtual elements.
Key Benefits of VR and AR in eLearning
- Immersive Engagement
Traditional eLearning platforms rely heavily on text, images, and videos. While effective, these formats often lack the interactivity necessary to sustain learner interest. VR and AR introduce immersive environments where learners are not just passive recipients but active participants.
For instance, a medical student can practice surgical procedures in a VR simulation, or a history student can explore an ancient civilization through AR-enhanced environments. Such experiences make learning more engaging and memorable.
- Safe Learning Environments
VR provides a risk-free platform for practicing high-stakes skills. Industries such as aviation, healthcare, and construction leverage VR for simulation-based training, where learners can make mistakes without real-world consequences. AR, on the other hand, provides real-time guidance and feedback in actual environments, enhancing on-the-job training.
- Personalized Learning
VR and AR cater to diverse learning styles. Kinesthetic learners, for example, thrive in environments where they can manipulate and interact with objects, a feature central to both VR and AR. Furthermore, these technologies allow instructors to tailor content based on learner performance, offering adaptive and personalized experiences.
- Global Access
Geographical boundaries no longer restrict learners. With VR and AR, students from around the globe can explore museums, attend virtual conferences, or collaborate in virtual classrooms. This democratization of education ensures equitable access to high-quality resources.
- Enhanced Retention Rates
Experiential learning improves retention. VR and AR create scenarios where learners can apply theoretical knowledge in practical settings, reinforcing learning outcomes. For example, AR applications in anatomy allow students to visualize and interact with 3D models of human organs, which is far more effective than studying 2D diagrams.
Applications of VR and AR in eLearning
- Corporate Training
Companies use VR to simulate challenging workplace scenarios, such as customer interactions or emergency drills. AR is utilized for just-in-time learning, where workers receive step-by-step guidance through AR-enabled devices.
- STEM Education
In science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, VR enables students to conduct experiments in virtual labs, while AR provides real-time visualizations of complex equations and models.
- Language Learning
VR immerses learners in virtual environments where they can practice conversational skills with AI-driven avatars. AR apps overlay translations or contextual information onto real-world objects, enhancing vocabulary acquisition.
- Cultural Exploration
Through VR, learners can virtually visit historic sites, experiencing cultures firsthand. AR enriches these experiences by overlaying historical information, animations, or audio guides onto the real world.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their advantages, VR and AR face certain challenges:
- Cost: High-quality VR headsets and AR devices can be expensive, making them inaccessible for some institutions.
- Technical Expertise: Developing VR and AR content requires specialized skills, which can be a barrier for smaller organizations.
- User Comfort: Extended use of VR headsets can lead to discomfort or motion sickness, which may hinder learning.
- Device Compatibility: AR applications often require modern smartphones or tablets, limiting access for users with older devices.
Future Trends in VR and AR eLearning
- AI Integration: Combining AI with VR and AR will allow for more intelligent and adaptive learning systems, tailoring content to individual needs and preferences.
- Haptic Feedback: The inclusion of haptic devices will enable learners to feel textures and movements in VR, enhancing the realism of simulations.
- 5G Connectivity: The widespread adoption of 5G will reduce latency, enabling smoother and more responsive VR and AR experiences.
- Collaborative VR/AR: Virtual classrooms and AR-enhanced group projects will foster collaboration among learners from diverse locations.
Conclusion
VR and AR are revolutionizing eLearning by making it more interactive, engaging, and effective. While challenges remain, the potential benefits far outweigh the limitations. As technology becomes more accessible and affordable, VR and AR are poised to become integral components of mainstream education, transforming how knowledge is delivered and absorbed. For learners and educators alike, the future of learning is not just digital—it’s immersive.
















